协同型过滤 ( Collaborative filtering)
一个协作型过滤算法通常的做法是对一大群人进行搜索,并从中找出与我们品味相近的一小群人。算法会对这些人所偏爱的其他内容进行考查,并将它们组合起来构造出一个经过排名的推荐列表。
一、相似度评价方法
0,数据集
本文中的数据集都是以嵌套字典的形式出现,如下:
字典的key为用户名,value为对各个物品的评价分数。
1 | users={'Lisa Rose': {'Lady in the Water': 2.5, 'Snakes on a Plane': 3.5, |
1,曼哈顿距离
最简单的距离计算方式是曼哈顿距离。在二维模型中,每个人都可以用(x, y)的点来表示,这里我用下标表示不同的人,(x1,y2)表示艾米,(x2,y2)表示神秘的X先生,那么他们之间的曼哈顿距离就是
Python实现:
1 | def sim_manhattan(rating1, rating2): |
2,欧几里德距离
对于二维模型,计算的是两点之间的直线距离。
对于N维模型,如下表:
@ | Angelica | Bill
-|-
Blues Traveler | 3.5 | 2
Broken Bells | 2 | 3.5
Deadmau5 | - | 4
Norah Jones | 4.5 | -
Phoenix | 5 | 2
Slightly Stoopid | 1.5 | 3.5
The Strokes | 2.5 | -
Vampire Weekend | 2 | 3
计算Angelica和Bill的欧几里得距离:
$$ Euclidean = \sqrt{(3.5-2)^2 + (2-3.5)^2+(5-2)^2+(1.5-3.5)^2+(2-3)^2} = 4.3 $$
Python实现:
1 | from math import sqrt |
3, 皮尔逊相关度评价
用户的问题
让我们仔细看看用户对乐队的评分,可以发现每个用户的打分标准非常不同:
Bill没有打出极端的分数,都在2至4分之间;
Jordyn似乎喜欢所有的乐队,打分都在4至5之间;
Hailey是一个有趣的人,他的分数不是1就是4。
那么,如何比较这些用户呢?解决方法之一是使用皮尔逊相关系数。
该计算系数是判断两组数据与某一直线拟合程度的一种度量。对应的公式比欧几里德距离评价的计算公式要复杂,但是它在数据不是很规范的时候(比如影评者对影片的评价总是相对于平均水平偏离很大时),会倾向于给出更好的结果。
我们先看下面的数据:
@ | Blues Traveler | Norah Jones | Phoenix | Strokes | Weird AI
-|-
Clara | 4.75 | 4.5 | 5 | 4.25 | 4
Robert | 4 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 1
这种现象在数据挖掘领域称为“分数膨胀”。Clara最低给了4分——她所有的打分都在4至5分之间。我们将它绘制成图表: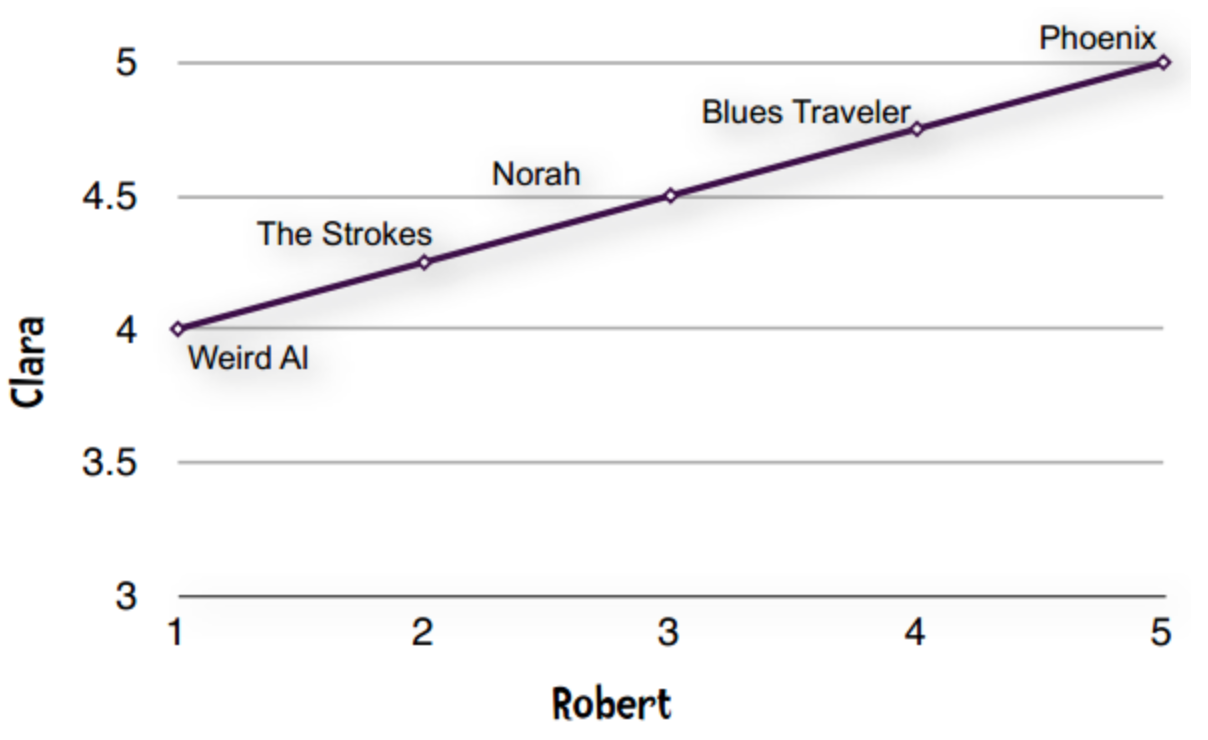
一条直线——完全吻合!!!
直线即表示Clara和Robert的偏好完全一致。他们都认为Phoenix是最好的乐队,然后是Blues Traveler、Norah Jones。如果Clara和Robert的意见不一致,那么落在直线上的点就越少。
皮尔逊相关系数的计算公式:
Python实现
1 | def sim_pearson(users, person1, person2): |
4,余弦相似度
它在文本挖掘中应用得较多,在协同过滤中也会使用到。这里记录了每个用户播放歌曲的次数,我们用这些数据进行推荐。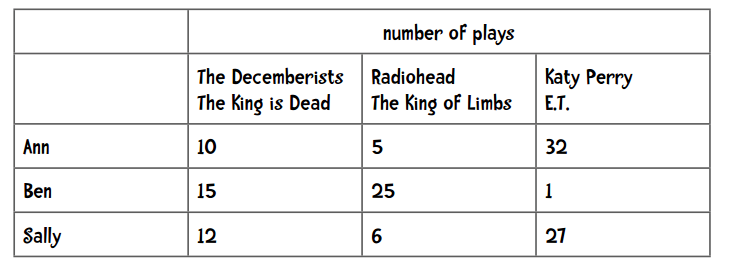
简单扫一眼上面的数据,我们可以发现Ann和Sally的偏好更为相似。
可以看到,Moonlight Sonata这首歌我播放了25次,但很有可能你一次都没有听过。事实上,上面列出的这些歌曲可能你一手都没听过。此外,iTunes上有1500万首音乐,而我只听过4000首。所以说单个用户的数据是稀疏的,因为非零值较总体要少得多。当我们用1500万首歌曲来比较两个用户时,很有可能他们之间没有任何交集,这样一来就无从计算他们之间的距离了。
余弦相似度的计算中会略过这些非零值。它的计算公式是:
$$ cos(x, y) = \dfrac{x\cdot y}{||x||\times||y||} $$
其中,“·”号表示数量积。“||x||”表示向量x的模,计算公式为:
对于下表:
@ | Blues Traveler | Norah Jones | Phoenix | Strokes | Weird AI
-|-
Clara | 4.75 | 4.5 | 5 | 4.25 | 4
Robert | 4 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 1
有两个向量:
1 | x = (4.75, 4.5, 5, 4.25, 4) |
它们的模是:
$$ ||x|| = \sqrt{4.75^2 + 4.5^2 + 5^2 + 4.25^2 + 4^2} = 10.09 $$
$$ ||y|| = \sqrt{4^2 + 3^2 + 5^2 + 2^2 + 1^2} = 7.416 $$
数量积的计算:
因此余弦相似度是:
$$ cos(x, y) = \dfrac{70}{10.093\times7.416} = 0.935 $$
5,应该使用哪种相似度?
如果数据存在“分数膨胀”问题,就使用皮尔逊相关系数
如果数据比较“密集”,变量之间基本都存在公有值,且这些距离数据是非常重要的,那就使用欧几里德或曼哈顿距离。
如果数据是稀疏的,则使用余弦相似度。
二、应用
1,推荐用户 —— K最邻近算法
使用K最邻近算法来找出K个最相似的用户。
1 | def top_matches(users, person, k=5, similarity=sim_pearson): |
2,推荐物品
通过一个经过加权的评价值来为影片打分,评论者的评分结果因此形成了先后的排名。
1 | def getRecommendations(users, person, similarity=sim_pearson): |